Overview
This article provides a comprehensive comparison of SMSF property loan lenders, focusing on the distinctions between banks and non-bank lenders regarding:
- Interest rates
- Flexibility
- Approval processes
While banks generally offer lower rates and enhanced security, non-bank lenders present more adaptable solutions and expedited approvals. This flexibility can be particularly advantageous for borrowers navigating unique financial circumstances, albeit often at a higher cost. Understanding these differences is crucial for making informed decisions that align with individual financial needs.
Introduction
In the evolving landscape of investment strategies, Self-Managed Super Fund (SMSF) property loans have emerged as a powerful avenue for individuals seeking to leverage their superannuation for real estate investments.
Are you looking to enhance your retirement savings? These loans present both opportunities and challenges within a complex regulatory framework.
As more investors turn to SMSF loans to diversify their portfolios, understanding the intricacies of lender options—from traditional banks to specialized non-bank lenders—becomes crucial.
This article delves into key considerations for selecting the right SMSF property loan lender, comparing the benefits and drawbacks of various lending institutions.
Furthermore, we provide insights into making informed financial decisions that align with your long-term investment goals.
Understanding SMSF Property Loans
Self-Managed Super Fund (SMSF) financing allows individuals to leverage their superannuation savings for the acquisition of investment real estate, and this is facilitated by SMSF property loan lenders in accordance with the guidelines set forth in the Superannuation Industry (Supervision) Act. This legislation mandates that the acquired asset must function solely as an investment, prohibiting personal use.
Typically structured under a limited recourse borrowing arrangement (LRBA), these financial products ensure that in the event of a default, the claim of the SMSF property loan lenders is confined exclusively to the asset financed by the advance, thereby protecting other SMSF resources. As we look towards 2025, the popularity of SMSF property loan lenders is witnessing a surge among investors eager to diversify their portfolios and enhance retirement savings through real estate. Recent trends reveal a heightened interest in these financial products, particularly from SMSF property loan lenders, fueled by the prospect of substantial tax advantages and the effective utilization of superannuation funds.
However, this landscape presents its own set of challenges; the complexities introduced by new regulations demand meticulous planning and professional guidance to ensure investments align with retirement objectives.
Experts emphasize the necessity of ongoing education and consultation with financial advisors to adeptly navigate the shifting market dynamics. Financial consultants assert that while self-managed superannuation fund real estate financing through SMSF property loan lenders offers considerable benefits, it also entails inherent risks that require careful management. Successful case studies illustrate how informed investors have harnessed self-managed superannuation fund financing with the help of SMSF property loan lenders to achieve their financial goals, underscoring the importance of staying abreast of compliance and management strategies to maximize tax benefits and avoid potential pitfalls.
With the right approach and support, SMSF property loan lenders can serve as a powerful avenue for wealth accumulation and a secure retirement through self-managed superannuation fund real estate financing.
Types of SMSF Property Loan Lenders: Banks vs. Non-Bank Lenders
In the realm of self-managed superannuation fund property financing, financial institutions can be categorized into two primary groups: banks and SMSF property loan lenders. Major Australian banks typically offer self-managed super fund financing, characterized by competitive interest rates and the reliability of established institutions. However, recent trends indicate that many SMSF property loan lenders have reduced their loan offerings, citing heightened perceived risks, which has led to a narrower selection for potential borrowers.
On the other hand, non-bank financial institutions, including specialized mortgage providers, have gained traction as SMSF property loan lenders in the SMSF lending landscape. These institutions often focus on niche markets, providing customized solutions that may include higher loan-to-value ratios (LVRs) and more adaptable lending criteria. While it is common for SMSF property loan lenders to impose higher interest rates, they frequently counterbalance this with expedited approval processes and a more personalized service experience. This distinction is crucial for borrowers to consider, as the choice between banks and non-bank entities can significantly impact their investment strategies and financial objectives.
Finance Story offers extensive access to a group of financiers, including specialized institutions and private backers, ensuring that small business proprietors can discover customized financial solutions that cater to their unique requirements.
For instance, utilizing self-managed superannuation funds for commercial real estate investments can be a strategic decision. Finance Story can assist in building a solid argument for adherence to self-managed super fund regulations, guiding borrowers through the process of selecting the appropriate SMSF property loan lenders for their commercial investment. Furthermore, Finance Story provides support in efficient post-settlement management, which involves establishing repayment schedules and directing rental income to the fund, ensuring compliance with regulations and maximizing returns.
As the demand for SMSF property loan lenders is anticipated to rise, particularly for commercial real estate, understanding the distinctions between these financing options will empower borrowers to make informed choices that align with their financial objectives. It is preferable to be proactive rather than allow a minor issue to escalate into a significant breach or financial problem. Therefore, it is crucial for borrowers to consult with brokers like Finance Story to clarify self-managed super fund regulations and ensure compliance.
Key Considerations for Selecting an SMSF Property Loan Lender
Selecting the right financial institution for a property mortgage requires a careful evaluation of several critical factors. Interest rates and fees are essential, as they can greatly impact the total cost of borrowing. As we look ahead to 2025, average interest rates for SMSF financing vary, making it crucial for borrowers to compare proposals from different providers to secure the most favorable terms.
Flexibility in financing terms stands out as another vital consideration. Borrowers should assess repayment options and loan-to-value ratio (LVR) limits, as these can vary significantly among financial institutions. A financier's experience and reputation in self-managed super fund lending are also pivotal; a respected financier is more likely to deliver quality service and support throughout the loan process.
Understanding the financial institution's evaluation criteria is paramount. Factors such as credit history and liquidity requirements must align with the SMSF's qualifications to facilitate a smooth approval process. Additionally, responsiveness and customer service are key indicators of a financial institution's reliability. A supportive lender can significantly enhance the borrowing experience, making it more efficient and less stressful.
It is noteworthy that there are fewer restrictions on commercial real estate investments compared to residential units, providing greater flexibility in investment choices. Categories of commercial assets eligible for investment through self-managed superannuation funds include office buildings, warehouses, and retail spaces.
Real-world examples underscore the importance of these considerations. A case study highlighted the adaptability of leveraging borrowed capital from self-managed superannuation fund financing for essential real estate repairs, emphasizing adherence to ATO regulations to avoid penalties. This illustrates the necessity for borrowers to prioritize essential improvements over unnecessary upgrades.
Professional guidance suggests that when selecting a loan provider for self-managed super funds, borrowers should concentrate on SMSF property loan lenders who demonstrate a solid understanding of regulations and offer competitive rates. As Theo Chambers noted, "Investing in property through your superannuation could be a powerful strategy to build wealth and secure your future." This perspective underscores the importance of making informed choices when navigating the self-managed super fund lending landscape. For personalized assistance, BOOK A CHAT with Finance Story to explore tailored guidance and support.
Comparative Analysis: Pros and Cons of Leading SMSF Lenders
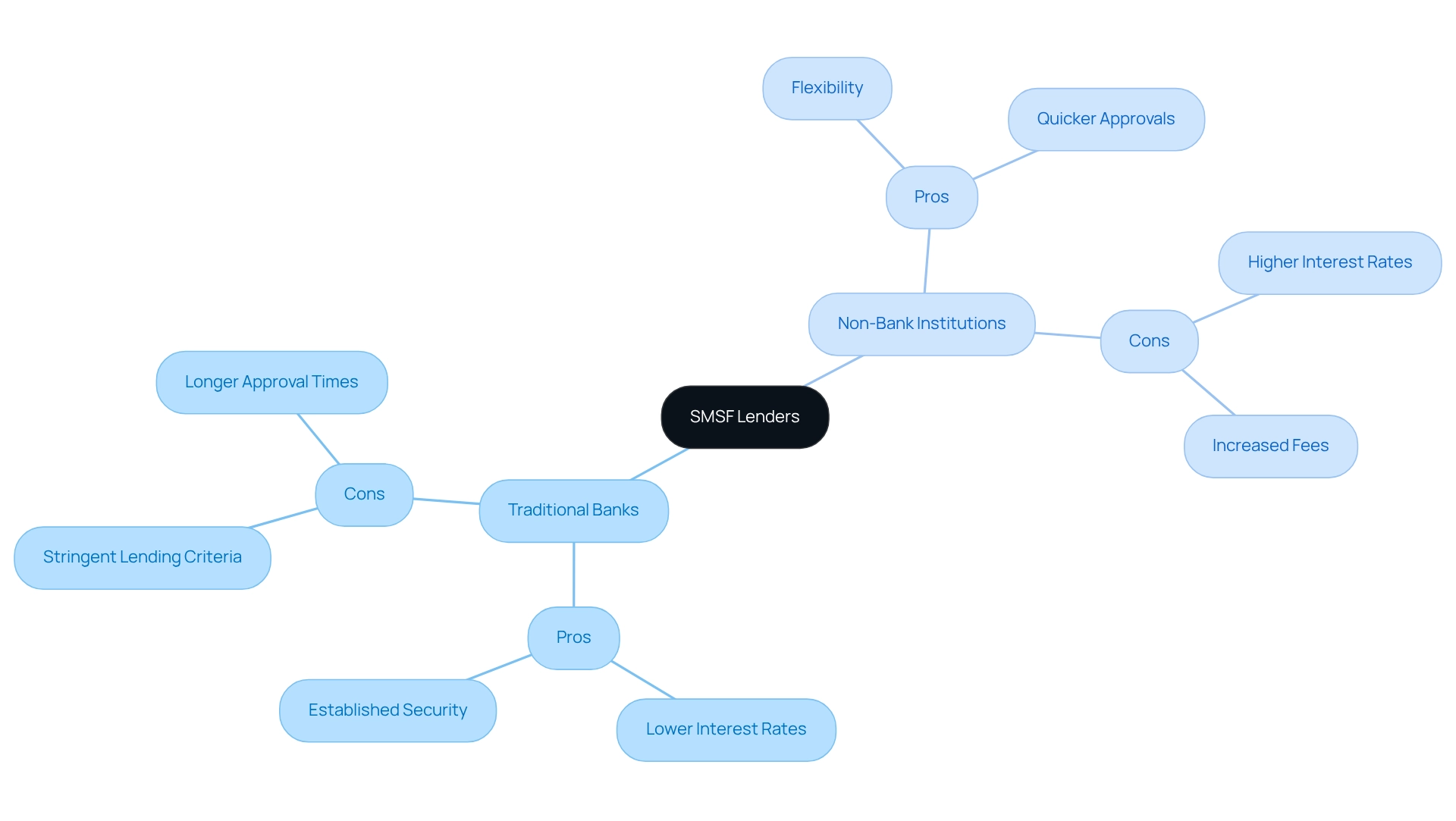
When assessing SMSF property loan lenders, a clear distinction emerges between traditional banks and non-bank institutions, each presenting unique advantages and challenges. Traditional banks often offer lower interest rates, appealing to long-term borrowers. Their established market presence provides a sense of security for clients. However, these institutions typically impose stringent lending criteria, which can be a barrier for borrowers with unconventional financial profiles or those seeking tailored solutions.
On the other hand, non-bank financial providers are known for their flexibility, often accommodating borrowers who may not fit the traditional mold. They tend to provide quicker approval processes, which can be crucial for clients looking to seize timely investment opportunities. Nevertheless, this convenience often comes at a cost, as non-bank institutions generally charge higher interest rates and fees, potentially increasing the overall expense of borrowing.
The financial implications of choosing non-bank institutions can be significant. While they may enable access to capital for individuals with distinct situations, the elevated expenses related to these financial products require thoughtful assessment of the long-term economic consequences. For example, the typical approval durations for self-managed super fund financing from non-bank sources can be significantly quicker than those from financial institutions, making them an appealing choice for urgent funding requirements.
It is essential to mention that self-managed super funds can invest in commercial real estate with fewer limitations compared to residential properties, which can be beneficial for small business proprietors. Current trends suggest that the self-managed superannuation fund credit sector is becoming more specialized, with additional SMSF property loan lenders entering the market to address various borrower requirements. This transition is backed by demographic alterations and an increasing interest from brokers, indicating that self-managed superannuation fund loans will keep rising in significance within the mortgage sector.
Ultimately, the choice between bank and non-bank self-managed superannuation fund providers depends on personal situations, including the borrower's financial profile, investment approach, and the particular conditions presented. As the SMSF lending market evolves, borrowers are encouraged to weigh the pros and cons carefully, ensuring that their choice aligns with their long-term financial goals. Finance Story is here to assist you in creating a strong case for compliance and lender selection, helping you navigate this complex landscape.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricacies of Self-Managed Super Fund (SMSF) property loans is essential for investors aiming to leverage their superannuation for real estate. These loans present a unique opportunity to diversify investment portfolios and enhance retirement savings. However, they also come with challenges and regulatory considerations that must be navigated carefully. Selecting the right lender—whether a traditional bank or a non-bank lender—is crucial, as this choice can significantly impact investment strategies and financial outcomes.
Key factors to consider include:
- Interest rates
- Loan terms
- The lender's experience in SMSF lending
Conducting thorough comparisons and seeking professional advice enables borrowers to make informed decisions that align with their long-term investment goals. The differences between banks and non-bank lenders underscore the need for a strategic approach; while banks may offer lower rates, non-bank lenders can provide the flexibility and speed that some investors require.
As the SMSF lending market continues to evolve, staying informed and proactive is crucial. With the right support and guidance, SMSF property loans can serve as a robust tool for building wealth and securing a prosperous retirement. Ultimately, the path to successful property investment through superannuation lies in understanding the available options and making choices that reflect individual financial aspirations.